 Getty Images
Getty ImagesBotox is a common and generally safe cosmetic treatment, but it has been found that long-term use can have lasting effects.
Is it a safe, surefire way to erase wrinkles and fine lines? Or a toxin that permanently locks your features into a “frozen” look? Either way, Botox is big business.
Botox ( Botulinum neurotoxins) is thought to be the most commonly performed cosmetic surgery procedure in the world, with around 3 million injections performed. Every yearOriginally derived from a powerful neurotoxin produced by bacteria, it works by blocking signals from the nerves that control the facial muscles, helping to relax the muscles and reduce fine lines and wrinkles, resulting in a more youthful looking face, which lasts for at least 3-4 months.
Most reported side effects are mild and temporary. They include pain at the injection site, swelling, and mild bruising, as well as headaches and flu-like symptoms for the first 24 hours. Temporary facial weakness and drooping also sometimes occur. happen.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesHowever, more severe reactions may also be observed. In April 2024, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that 22 women aged 25 to 59 had recently died of “Adverse reactions” Counterfeiting or mishandling Botox.
Eleven people were hospitalized and six were treated with antitoxin over concerns of botulism, a disease in which the toxin attacks the central nervous system and causes muscle damage. paralysisIt can cause breathing difficulties and even death.
Reported symptoms include blurred or double vision, drooping eyelids, difficulty swallowing, slurred speech, difficulty breathing, fatigue and weakness. All 22 cases occurred after the women received Botox injections in non-medical settings from unqualified or untrained individuals.
“CDC, F.D.A. [Federal Drug Administration]”Authorities are actively investigating these illnesses that occurred after injections of improperly handled or counterfeit botulinum toxin,” said Michelle Waltenberg, an epidemiologist in the CDC's Division of Communicable Disease Epidemiology.
But how common are these side effects?
“If botulinum toxin is properly manufactured and a good brand, it's strong enough that even if it spreads a little, it doesn't cause any major side effects,” says Ash Mosahevi, professor of plastic surgery at University College London.
“The dosage is extremely low; that amount of toxin is not enough to cause botulism in humans. But the problem is that there are questionable counterfeits out there that are poorly made, poorly manufactured and poorly controlled.”
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesWhat is Botox?
Botulinum neurotoxins are highly lethal poisons produced by bacteria. BotulinumThey enter neurons and bind to vesicles carrying the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (Ach), preventing its release.
Ach causes muscle contraction, whereas botulinum toxin causes muscle paralysis. There are seven different forms of botulinum toxin, types A-G.
Fake Botox is bad news, but what about the safety of regular botulinum toxin? 2020 Survey A review of the safety of cosmetic Botox injections concluded that serious side effects like those reported by the CDC are rare. For example, between 2002 and 2003, 36 serious side effects There have been numerous reports to the FDA regarding the use of cosmetics, most of which are Difficulty swallowingThe risk of serious side effects 33 times higher Botox is used for therapeutic rather than cosmetic purposes (Botox may be used to treat conditions such as migraines, neck spasms, sweating, overactive bladder and poor eyesight).
However, it may simply be that side effects have not been reported. 2023 Survey A survey by Mosahevi and colleagues at University College London found that 69% of respondents had experienced long-term side effects from Botox, including pain, anxiety and headaches. When the procedure went wrong, patients could suffer serious psychological and emotional consequences.
“If administered incorrectly, it can cause symptoms like droopy eyelids that can last for six months,” Mosahevi said.
“It can have long-term effects, including embarrassment in the workplace and loss of self-confidence.”
Long-term effects
Little is known about the long-term health effects of Botox, as most clinical trials only follow patients for around six months. However, some studies have shown that long-term use of botulinum toxin for cosmetic purposes can be Permanent changes Your facial expression changes and you are unable to move your facial muscles. 2022 Review Survey It was found that people who received regular Botox injections saw changes in muscle structure, function and appearance up to four years after their last injection.
“If you don't use your abdominal muscles [abdominal muscles] If you do that for 10 years, it will start to weaken,” Mosahevi said.
“Similarly, if the muscles that cause facial wrinkles are not used or are paralyzed by Botox, after a while they will not be as strong as they were before, resulting in a less expressive face.”
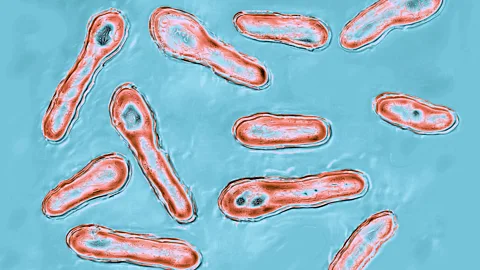
It's also possible that the Botox toxin can escape from nerve endings close to muscles and travel to the wider central nervous system. In 2015, scientists led by Frederic Meunier at the University of Queensland in Australia used cutting-edge microscopes to observe single molecules of botulinum toxin. Move at high speed Botulinum toxin travels along rat neurons. It was previously thought that botulinum toxin would remain in the nerve endings of neurons where neurotransmitter release occurs before being broken down. However, this was not the case.
“We observed that some of the toxin molecules enter the nerve terminal and are transported along the axon to the cell body, where they are degraded,” Meunier says.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesSome of the transported toxin escaped to other neurons by an unknown mechanism.
“As far as we know, the only toxin that does this is tetanus toxin, which travels along motor neurons to the spinal cord, where it blocks transmission,” Meunier says.
However, it's important to note that the concentration of botulinum toxin used in the study was much higher than that used in Botox injections, Meunier added.
“In humans, this way of thinking [the toxin] It is unlikely that it will have effects that reach back to the central nervous system.”
But there's also evidence that long-term use of Botox can have psychological effects on patients. In a 2023 study, neurologist Mitchell Brin of the University of California, Irvine, and his colleagues found that Brain scanned In a study of 10 women before and after receiving Botox injections, subjects underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging of their brains while being shown pictures of angry and happy faces alternating with pictures of neutral faces. Scans after Botox showed changes in activity in two areas of the brain known to be involved in emotion processing: the amygdala and the fusiform gyrus.
this is, Other studiesIt has been shown that receiving Botox injections may make it harder for people to recognise and process the emotions of others.
A 2023 study suggests the explanation could be the way our brains perceive other people's emotions. For example, when we see someone else's happy or sad facial expression, we unconsciously use our own facial muscles to mimic it. This helps us understand and interpret the feelings of others.
However, because Botox paralyzes the facial muscles, it can reduce your ability to imitate other people's facial expressions, potentially making you less empathetic.
So what can you do to minimize the risks of Botox injections? Firstly, Botox injections should only be received, ideally in a medical setting, from a licensed provider who is trained in how to administer Botox.
In a statement to BBC Future, Allergan Aesthetics, the maker of Botox, said users should only undergo the treatment under the supervision of a qualified medical professional.
A company spokesman added: “Our top priority is the health and safety of our patients and all reports of counterfeit products are thoroughly investigated by our team, in collaboration with law enforcement and regulators.”
“We have rigorous and sophisticated manufacturing and distribution processes to ensure the quality and authenticity of our products, including rigorous anti-counterfeiting features.”
Mosahebi recently analysed the UK cosmetic injection industry and found that 68% of cosmetic practitioners who administer injections such as Botox Not a doctor.
However, there is every reason to believe that Botox is largely safe when administered correctly.
“It's really widely used and has great safety features,” Meunier said.
“Some people have experienced side effects, but you have to consider the millions of people who have ingested this toxin since the 1980s and 1990s.”


